Eight Robots Rearranging Shelves

An exciting frontier in robotic manipulation is the use of multiple arms at once. However, planning concurrent motions is a challenging task using current methods. The high-dimensional composite state space renders many well-known motion planning algorithms intractable. Recently, Multi-Agent Path-Finding (MAPF) algorithms have shown promise in discrete 2D domains, providing rigorous guarantees. However, widely used conflict-based methods in MAPF assume an efficient single-agent motion planner. This poses challenges in adapting them to manipulation cases where this assumption does not hold, due to the high dimensionality of configuration spaces and the computational bottlenecks associated with collision checking. To this end, we propose an approach for accelerating conflict-based search algorithms by leveraging their repetitive and incremental nature -- making them tractable for use in complex scenarios involving multi-arm coordination in obstacle-laden environments. We show that our method preserves completeness and bounded sub-optimality guarantees, and demonstrate its practical efficacy through a set of experiments with up to 10 robotic arms.
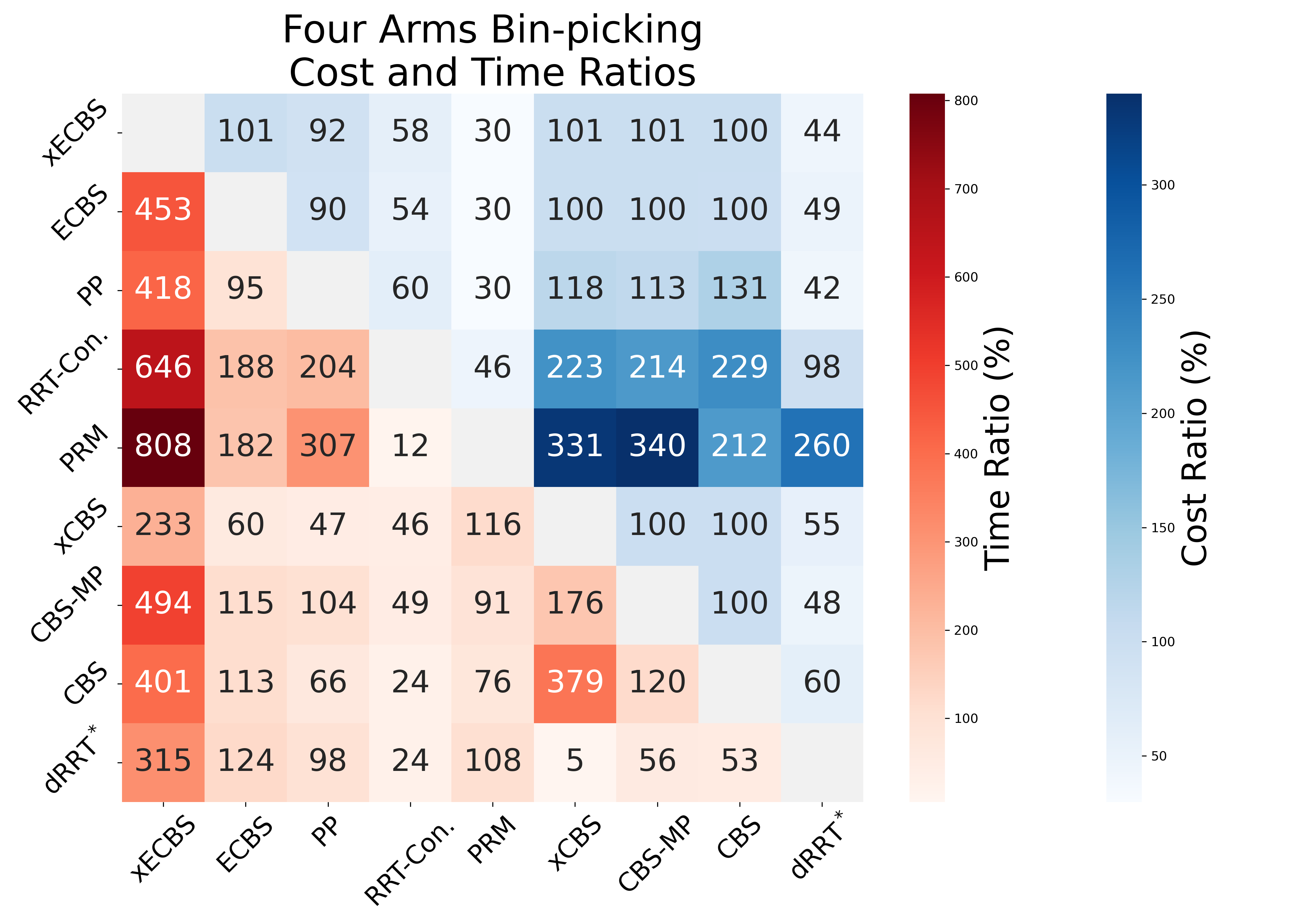
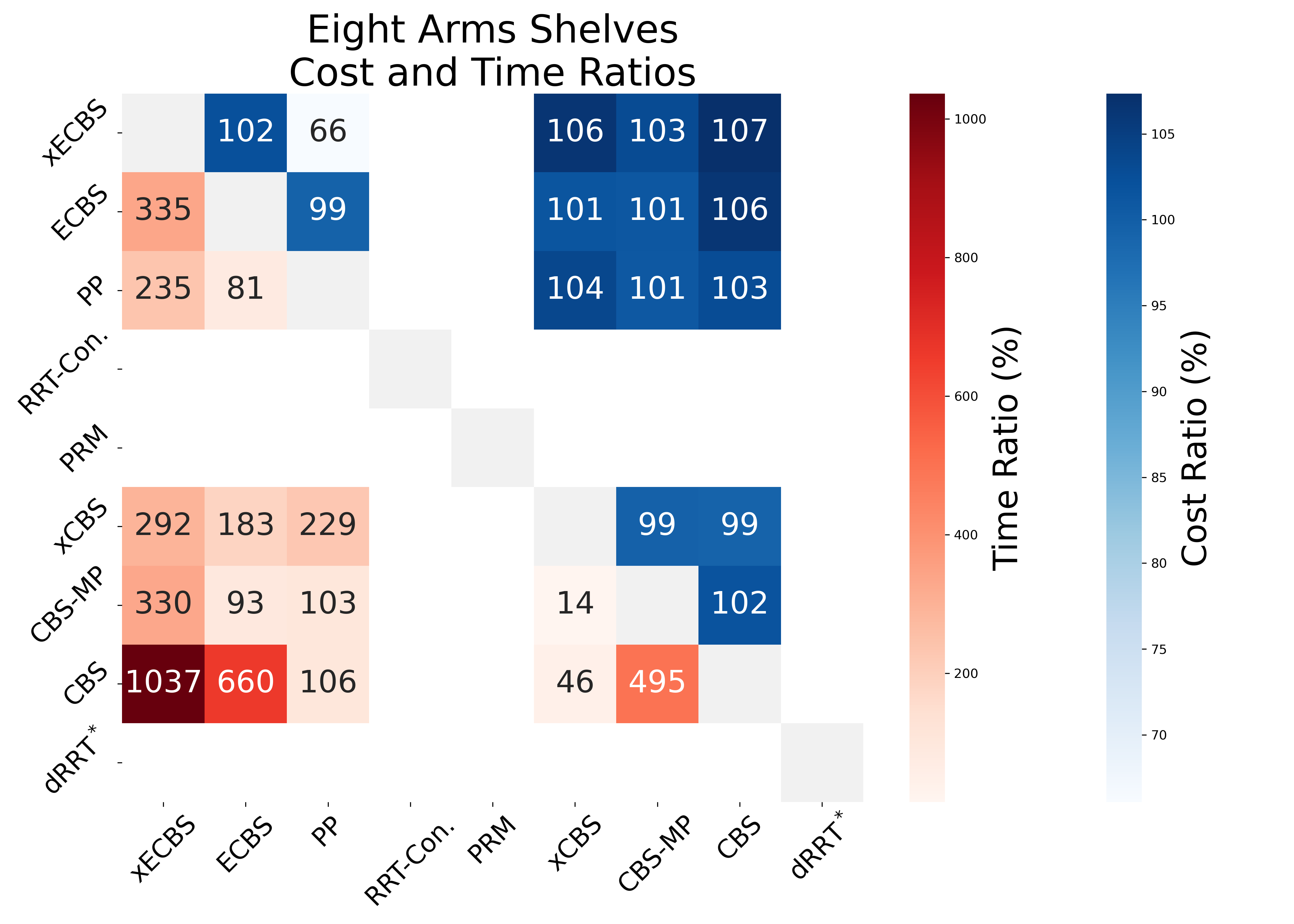
Applying accelerated search-based planning to real world manipulation tasks shows promise. Experience Accelerated ECBS, xECBS, succeeds in 84% of the shelf-rearrangement trials, with the second best method succeeds in 40% of the trials. In bin-picking with 4 arms, sampling-based methods yield suboptimal solutions and xECBS maintains low-costs.